[자바기초] 2차원 배열(2D Array)

[자바기초] 2차원 배열(2D Array)
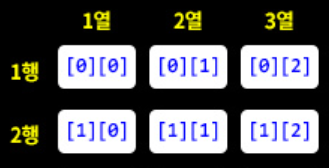
[1] 2차원 배열이란?
- 배열 안에 다시 배열이 들어 있는 구조
- 초기화 하지 않을 경우 0, 0.0, false 등의 자료형에 맞춰 저장됨.
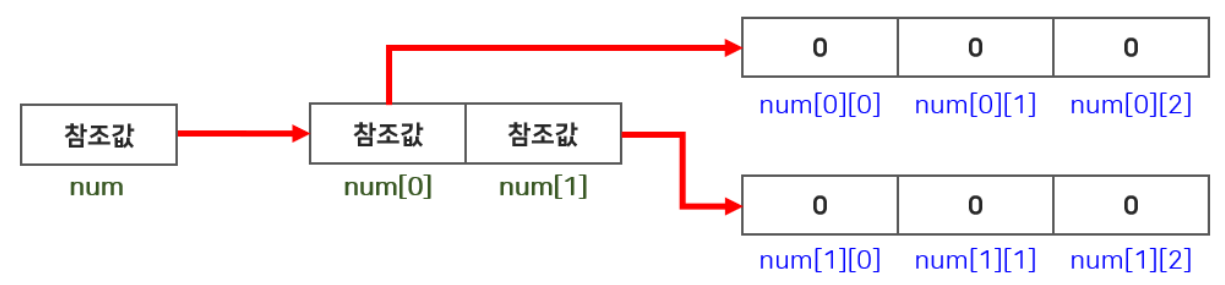
- 2차원 배열의 크기: 행의 수는 배열명.length, 열의 수는 배열명[행 index].length
[예제1] 2차원 배열의 선언, 초기화, 크기(length)에 대해서 알아보자.
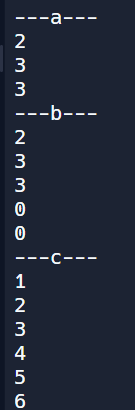
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 2차원 배열 선언 3가지 방법 int[][] a; //int[] a[]; //int a[][]; a = new int[2][3]; int[][] b = new int[2][3]; int[][] c = {{1,2,3}, {4,5,6}}; // array a System.out.println("---a---"); System.out.println(a.length); System.out.println(a[0].length); System.out.println(a[1].length); // array b System.out.println("---b---"); System.out.println(b.length); System.out.println(b[0].length); System.out.println(b[1].length); System.out.println(b[0][0]); System.out.println(b[0][1]); // array c System.out.println("---c---"); System.out.println(c[0][0]); System.out.println(c[0][1]); System.out.println(c[0][2]); System.out.println(c[1][0]); System.out.println(c[1][1]); System.out.println(c[1][2]); } } | cs |
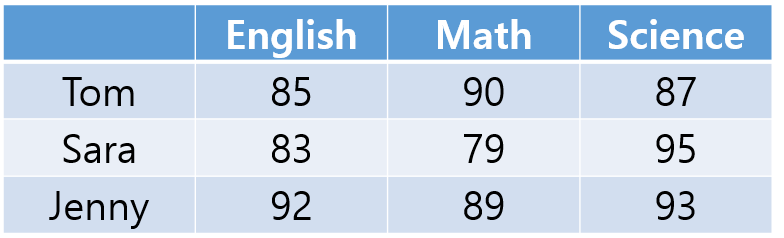
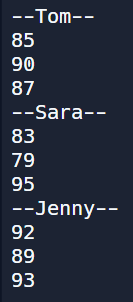
[유제1] 아래의 성적표를 2차원 배열(3행 3열)로 저장하세요. 그리고 아래 그림과 같이 배열의 요소를 반복문 사용없이 println()구문으로 하나씩 출력하세요.
[예제2] 자바 2차원 배열 요소를 초기화 하고, 각 요소의 합을 for 반복문으로 계산하고 결과를 출력하는 아래 예제를 살펴봅시다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] a = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } }; // 배열 선언 및 초기화 int sum = 0; // 배열의 요소 합계를 저장할 변수 int sumOfa1 = 0; // 배열의 1행 요소 합계를 저장할 변수 int sumOfa2 = 0; // 배열의 2행 요소 합계를 저장할 변수 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { sum += a[i][j]; // sum = sum + a[i][j] // 배열 전체 요소 합하기 if(i == 0) sumOfa1 += a[0][j]; // 배열 1행 요소 합치기 if(i == 1) sumOfa2 += a[1][j]; // 배열 2행 요소 합치기 System.out.println("a[" + i + "][" + j + "] : " + a[i][j]); } } // 합 출력 System.out.println("sum: " + sum); System.out.println("sumOfa1: " + sumOfa1); System.out.println("sumOfa2: " + sumOfa2); } } | cs |
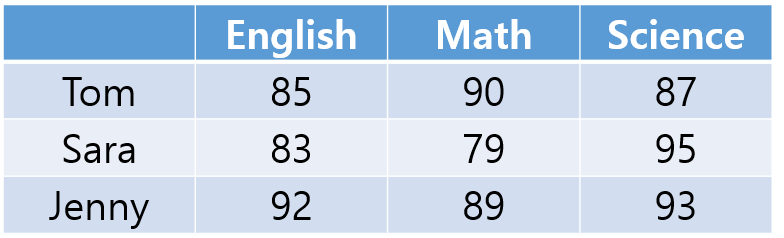
[유제2] English, Math, Science 3과목에 대한 3 명의 학생(Tom, Sara, Jenny)의 성적이 아래와 같이 나와있습니다.
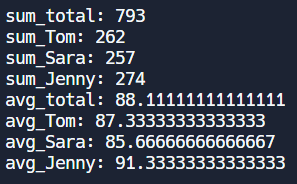
정수형 2차원 배열을 하나 만들고 아래의 성적으로 초기화 해주세요. 그리고 3명의 학생의 성적 합, 그리고 각 학생의 성적의 합과 평균을 아래 그림과 같이 출력되게 코딩하세요.
[예제3] 2차원 배열의 행(row)에 따라, 불규칙한 개수인 열(column)을 만들 수도 있다. 아래의 예제를 살펴보세요.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] s = {{1,2}, {3,4,5,6}, {7,8,9}}; // 불규칙한 열 개수 2차원 배열 for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(s[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } | cs |
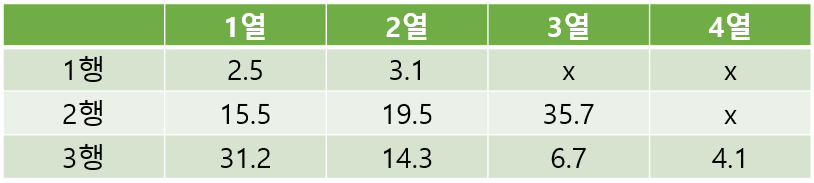
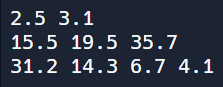
[유제3] 아래 표의 데이터를 double형 2차원 배열에 초기화 하여 입력하세요. 그리고 이 배열의 모든 요소를 for 반복문으로 아래 그림과 같이 출력해주세요.
[예제4] 2차원 배열의 행(row), 열(column) 개수를 입력받고, 그렇게 만들어진 배열의 요소도 하나씩 키보드로 입력받으세요. 그리고 마지막에 배열의 모든 요소값을 아래와 같이 출력해 봅니다.
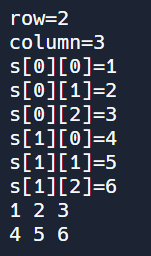
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int row, column; System.out.print("row="); row = scan.nextInt(); // 행 개수 System.out.print("column="); column = scan.nextInt(); // 열 개수 int [][] s = new int[row][column]; for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print("s["+i+"]["+j+"]="); s[i][j] = scan.nextInt(); // 배열 요소에 키보드 입력받기 } } // 2차원 배열 요소 모두 출력 for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(s[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } | cs |
[유제4] 위 예제4번의 코드를 전혀 보지않고, 스스로 생각하며 코딩을 똑같이 해보세요.
*유제 정답 확인(아래 "더보기" 클릭)
[유제1 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] s = {{85,90,87}, {83,79,95}, {92,89,93}}; System.out.println("--Tom--"); System.out.println(s[0][0]); System.out.println(s[0][1]); System.out.println(s[0][2]); System.out.println("--Sara--"); System.out.println(s[1][0]); System.out.println(s[1][1]); System.out.println(s[1][2]); System.out.println("--Jenny--"); System.out.println(s[2][0]); System.out.println(s[2][1]); System.out.println(s[2][2]); } } | cs |
[유제2 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] score = { { 85,90,87 }, { 83,79,95 }, {92,89,93} }; int sum_Tom = 0; int sum_Sara = 0; int sum_Jenny = 0; int sum_total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < score[i].length; j++) { sum_total += score[i][j]; if(i == 0) sum_Tom += score[i][j]; // Tom if(i == 1) sum_Sara += score[i][j]; // Sara if(i == 2) sum_Jenny += score[i][j]; // Jenny } } // 합 출력 System.out.println("sum_total: " + sum_total); System.out.println("sum_Tom: " + sum_Tom); System.out.println("sum_Sara: " + sum_Sara); System.out.println("sum_Jenny: " + sum_Jenny); // 평균 출력 System.out.println("avg_total: " + (double)sum_total / 9); System.out.println("avg_total: " + (double)sum_Tom / 3); System.out.println("avg_total: " + (double)sum_Sara / 3); System.out.println("avg_total: " + (double)sum_Jenny / 3); } } | cs |
[유제3 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { double[][] s = {{2.5,3.1}, {15.5,19.5,35.7}, {31.2,14.3,6.7,4.1}}; for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(s[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } | cs |
[유제4 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int row, column; System.out.print("row="); row = scan.nextInt(); // 행 개수 System.out.print("column="); column = scan.nextInt(); // 열 개수 int [][] s = new int[row][column]; for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print("s["+i+"]["+j+"]="); s[i][j] = scan.nextInt(); // 배열 요소에 키보드 입력받기 } } // 2차원 배열 요소 모두 출력 for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < s[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(s[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } | cs |