반응형

[자바기초.010] Traversing ArrayList(리스트 반복문)
[1] Traversing ArrayList
- ArrayLists can be traversed with while loops
- Both regular and enhanced for loops much the same way we use those constructs to loop over an array.
[2] Enhanced for loop with ArrayList
- You can’t use the enhanced for loop if you want to add or remove elements while traversing an ArrayList.
- If an ArrayList is modified, such as by calling the add or remove methods, while it is being looped over, it will cause the loop to throw a ConcurrentModificationException.
- If you need to modify an ArrayList while looping over it, you’ll need to use a regular while or for loop.
[예제1] Enhanced for each 반복문을 이용하여 ArrayList를 순회(Traversing)하며서 리스트의 모든 요소를 더하는 코드입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); myList.add(50); myList.add(30); myList.add(20); int total = 0; for (Integer value : myList) { total += value; } System.out.println("Sum of all elements: " + total); // Write a for-each loop that computes the product // of all the elements in myList and print out the product. } } | cs |
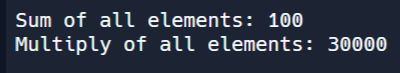
[유제1] 위 코드에서 ArrayList의 모든 요소를 곱하고, 그 결과를 아래와 같이 출력하는 코드를 추가해 보세요.
[예제2] Regular for 반복문을 이용해 ArrayList를 순회(Traversing)하며 숫자 입력을 받고 모든 요소의 합을 구하는 코드입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.print("index " + i + ": "); int input = scan.nextInt(); myList.add(input); } for(int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) { total = total + myList.get(i); } System.out.println("Total is " + total); } } | cs |
- ArrayList의 index도 0부터 시작한다. 저장된 요소의 마지막 index는 .size() -1 이다.
- 배열은 요소에 접근하기 위해 배열이름[index]를 사용하지만, ArrayList는 .get(index) method를 사용하여 요소의 값을 가져오고, .set(index,value) 을 이용해 특정값을 저장한다.
- ArrayList의 index 범위를 넘어서면,IndexOutOfBoundsException 에러가 발생한다.
[유제2] 위의 예제 코드처럼 String형 ArrayList 하나를 만드세요. 그리고 이 리스트에 for문을 이용해 "Tom", "Jane", "Bob" 문자열 3개를 키보드로 입력 받아 저장하세요. 마지막에도 for문을 이용해 이 리스트의 요소를 아래와 같이 출력하세요.

[예제3] Object-Oriented Programming 방식으로 ArrayList에 저장된 문자열을 삭제하는 코드입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | // ListWorker.java import java.util.ArrayList; public class ListWorker { ArrayList<String> nameList; // Constructor(생성자) public ListWorker(ArrayList<String> nameList) { this.nameList = nameList; } public boolean removeName(String name) { boolean found = false; // false at first time. int index = 0; while (index < nameList.size()) { if (name.equals(nameList.get(index))) { nameList.remove(index); found = true; // true after found name } else { index++; } } return found; } } | cs |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | // Main.java import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>(); myList.add("Amun"); myList.add("Ethan"); myList.add("Donnie"); myList.add("Ethan"); ListWorker listWorker = new ListWorker(myList); System.out.println(listWorker.nameList); listWorker.removeName("Ethan"); System.out.println("After removing Ethan: " + listWorker.nameList); } } | cs |
[유제3] 위 코드에서 다음의 조건을 만족하는 코드를 추가하세요.
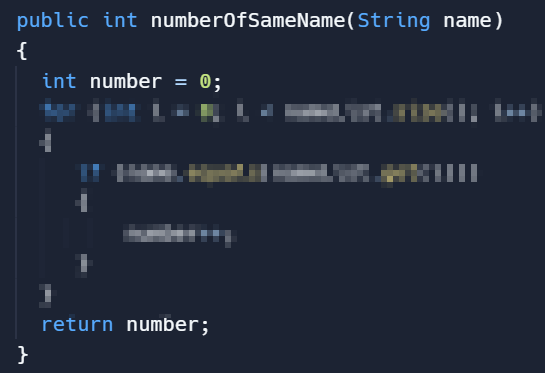
- ListWorker.java에 리스트 속의 사람이름이 몇 개 있는지 개수를 되돌려주는 메소드를 추가합니다.
- 아래의 코드처럼 코딩하되, 모자이크 처리로 안보이는 부분을 채우면 됩니다.
[ListWorker.java 클래스에 추가할 메소드]
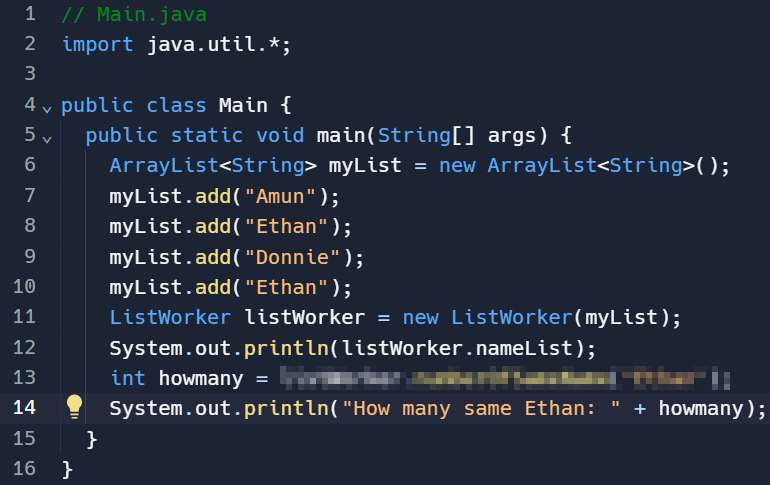
[Main 클래스의 main 메소드]
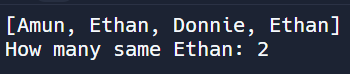
[위 코드 실행 결과]
[예제4] 아래의 코드는 무슨 동작을 하는 건지 설명해 보세요.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // Main.java import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { arr.add(i); } System.out.println(arr); for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) { System.out.println("Removing element " + i + " : " + arr.get(i)); arr.remove(i); } } System.out.println(arr); } } | cs |
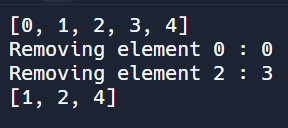
- The upper code is supposed to initialize the ArrayList arr to [0,1,2,3,4] and then remove every other element to get [1,3].
- However, when you remove an element the size of the array changes and elements move up an index!
- See if you can figure out why you get the unexpected result.
- If you use add or remove inside a loop that traverses an ArrayList, you may get unexpected results because the size of the ArrayList has changed!
[유제4] 아래 코드를 어떤 기능을 하는 건지 말해봅시다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // Main.java import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> test1Grades = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer> test2Grades = new ArrayList<Integer>(); test1Grades.add(100); test2Grades.add(100); test1Grades.add(85); test2Grades.add(74); test1Grades.add(73); test2Grades.add(91); double total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < test1Grades.size(); i++) { total += test1Grades.get(i) + test2Grades.get(i); } int numberOfGrades = test1Grades.size() * 2; System.out.println("Average over two tests: " + (int) total / numberOfGrades); } } | cs |
[유제 정답은 아래 "더보기" 클릭]
더보기
[유제1 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); myList.add(50); myList.add(30); myList.add(20); int total = 0; int multiply = 1; for (Integer value : myList) { total += value; multiply *= value; } System.out.println("Sum of all elements: " + total); System.out.println("Multiply of all elements: " + multiply); // Write a for-each loop that computes the product // of all the elements in myList and print out the product. } } | cs |
[유제2 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>(); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.print("Name " + i + ": "); String input = scan.nextLine(); myList.add(input); } for(int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) { System.out.println("Hello ~ " + myList.get(i)); } } } | cs |
[유제3 정답]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | // ListWorker.java import java.util.ArrayList; public class ListWorker { ArrayList<String> nameList; // Constructor(생성자) public ListWorker(ArrayList<String> nameList) { this.nameList = nameList; } public boolean removeName(String name) { boolean found = false; // false at first time. int index = 0; while (index < nameList.size()) { if (name.equals(nameList.get(index))) { nameList.remove(index); found = true; // true after found name } else { index++; } } return found; } // 유제3 정답 메소드 public int numberOfSameName(String name) { int number = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nameList.size(); i++) { if (name.equals(nameList.get(i))) { number++; } } return number; } } | cs |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | // Main.java import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>(); myList.add("Amun"); myList.add("Ethan"); myList.add("Donnie"); myList.add("Ethan"); ListWorker listWorker = new ListWorker(myList); System.out.println(listWorker.nameList); int howmany = listWorker.numberOfSameName("Ethan"); System.out.println("How many same Ethan: " + howmany); } } | cs |
[유제4 정답]
728x90
반응형
'자바(Java) > 자바기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바기초.012] 상속(Inheritance) (0) | 2024.03.13 |
|---|---|
| [자바기초.011] 배열과 리스트 비교(Array vs List) (0) | 2024.03.13 |
| [자바기초] List & ArrayList (0) | 2024.03.10 |
| [자바기초] 2차원 배열(2D Array) (0) | 2024.03.03 |
| [자바기초]1차원 배열(array) (0) | 2024.03.01 |




댓글